Difference between revisions of "Liquid Paginate Tag"
From Spiffy Stores Knowledge Base
(→Usage) |
(→Usage) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
To use pagination you have to wrap a '''paginate''' tag around the '''for''' loop which iterates over your collection. The '''paginate''' tag will figure out all the calculations by itself and make sure that further calls to the collection will return with the correct items in the correct order. | To use pagination you have to wrap a '''paginate''' tag around the '''for''' loop which iterates over your collection. The '''paginate''' tag will figure out all the calculations by itself and make sure that further calls to the collection will return with the correct items in the correct order. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Paginate1.jpg]] | [[Image:Paginate1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
=== The Paginate Object === | === The Paginate Object === | ||
| − | Within the paginate block you have access to the paginate object which | + | Within the '''paginate''' block you have access to the paginate object which contains the following information: |
| − | + | * paginate.page_size - The number of items displayed on each page. | |
| − | + | * paginate.current_page - The page currently being displayed. | |
| − | + | * paginate.current_offset - The number of items skipped so far. | |
| − | + | * paginate.pages - Total number of pages. | |
| − | + | * paginate.items - Total number of items in this collection. | |
| − | + | * paginate.previous - The previous page, if it exists. | |
| − | + | ** paginate.previous.title - Title of the previous link. | |
| − | + | ** paginate.previous.url - URL of the previous link. | |
| − | + | * paginate.next - The next page, if it exists. | |
| − | + | ** paginate.next.title - Title of the next link. | |
| − | + | ** paginate.next.url - URL of the next link. | |
| − | + | * paginate.parts - An array of all the parts which make up the navigation for this pagination. Each element will have these three elements: | |
| − | + | ** part.is_link - Is this part a link? | |
| − | + | ** part.title - Link Title | |
| − | + | ** part.url - Link URL | |
== Displaying the pagination navigation == | == Displaying the pagination navigation == | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 17 June 2008
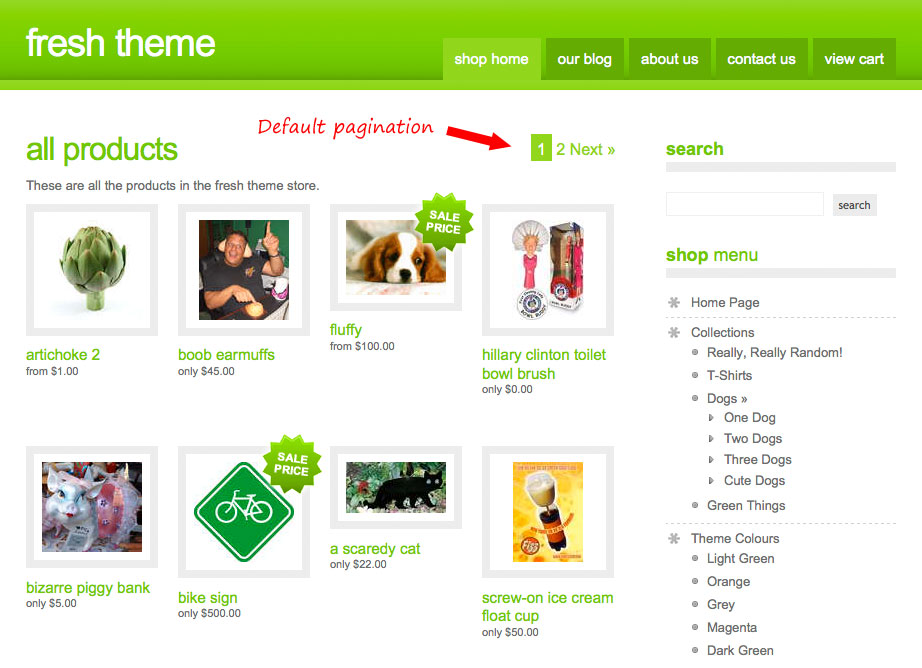
The paginate tag is responsible for pagination within a Spiffy Stores template. It's currently applicable to collections, products and blog articles. By default the default limit of items that can be show is 50, so if you want to show more, then you'll need to use the paginate tag.
The built-in themes automatically use paginate for collections and blog pages.
Contents
Usage
To use pagination you have to wrap a paginate tag around the for loop which iterates over your collection. The paginate tag will figure out all the calculations by itself and make sure that further calls to the collection will return with the correct items in the correct order.
{% paginate collection.products by 6 %}
{% for product in collection.products %}
{{ product.title }}
{% endfor %}
{% endpaginate %}
The Paginate Object
Within the paginate block you have access to the paginate object which contains the following information:
- paginate.page_size - The number of items displayed on each page.
- paginate.current_page - The page currently being displayed.
- paginate.current_offset - The number of items skipped so far.
- paginate.pages - Total number of pages.
- paginate.items - Total number of items in this collection.
- paginate.previous - The previous page, if it exists.
- paginate.previous.title - Title of the previous link.
- paginate.previous.url - URL of the previous link.
- paginate.next - The next page, if it exists.
- paginate.next.title - Title of the next link.
- paginate.next.url - URL of the next link.
- paginate.parts - An array of all the parts which make up the navigation for this pagination. Each element will have these three elements:
- part.is_link - Is this part a link?
- part.title - Link Title
- part.url - Link URL
Manually using pagination
<div id="pagination">
{% if paginate.previous %}
{{ paginate.previous.title | link_to: paginate.previous.url }}
{% endif %}
{% for part in paginate.parts %}
{% if part.is_link %}
{{ part.title | link_to: part.url }}
{% else %}
{{ part.title }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% if paginate.next %}
{{ paginate.next.title | link_to: paginate.next.url }}
{% endif %}
</div>
The easy way:
The paginate tag will add a new paginate variable to your view from which all vital parameters for pagination can be extracted. If you just want to get a good standard pagination going you can take this paginate variable and pipe it into the filter default_pagination which will leave you with attractive looking and fully functional pagination
{% paginate collection.products by 5 %}
{% for product in collection.products %}
{{ product.title }}
{% endfor %}
<div id="pagination">
{{ paginate | default_pagination }}
</div>
{% endpaginate %}